(!)Due to Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended environment.
Mon. - Fri. 8 a.m. - 6 p.m.
All Categories
-
Automation Components
Automation Components
Show all categories of Automation Components-
Linear Motion
-
Rotary Motion
-
Connecting Parts
-
Rotary Power Transmission
-
Motors
-
Conveyors & Material Handling
-
Locating, Positioning, Jigs & Fixtures
-
Inspection
-
Sensors, Switches
-
Pneumatics, Hydraulics
-
Vacuum Components
-
Hydraulic Equipment
-
Spray Equipment And Accessories
-
Pipe, Tubes, Hoses & Fittings
-
Modules, Units
-
Heaters, Temperature Control
-
Aluminum Extrusions, Framing, Support & Posts
-
Casters, Leveling Mounts, Posts
-
Doors, Cabinet Hardware
-
Springs, Shock Absorbers
-
Adjustment/Fastening Components, Pins, Magnets
-
Antivibration, Soundproofing Materials, Safety Products
-
- Fasteners
- Materials
-
Wiring Components
Wiring Components
Show all categories of Wiring Components-
LAN Cables / Industrial Network Cables
-
Equipment Specific Cables
-
Cordsets
-
Computer & AV Cables
-
Wire/Cable
-
Connector (General Purpose)
-
Crimp Terminal Components
-
Cable Organization
-
Cable Gland Components
-
Cable Bushing/Clip/Sticker
-
Screw/Spacer
-
Cable accessories
-
Tube
-
Electrical Conduits
-
Duct/Wiring
-
Electrical Wiring Tools
-
Dedicated tools
-
Soldering supplies
-
- Electrical & Controls
-
Cutting Tools
Cutting Tools
Show all categories of Cutting Tools-
Carbide End Mill
-
HSS End Mill
-
Concrete Drill Bits
-
Milling Cutter Insert / Holder
-
Core Drill Bits
-
Customized Straight Blade End Mill
-
Dedicated Cutter
-
Crinkey Cutters
-
Turning Tool
-
Drill
-
Cutting Tool Accessories
-
Screw Hole Related Tools
-
Reamer
-
Electric Drill Bits
-
Chamfering, Centering Tool
-
Hole Saws
-
Magnetic Drill Press Cutters
-
Step Drills
-
Wood Drills & Cutters
-
-
Processing Tools
-
Packing & Logistics Storage Supplies
- Safety Products
-
Research and Development & Cleanroom Supplies
Research and Development & Cleanroom Supplies
Show all categories of Research and Development & Cleanroom Supplies - Press Die Components
-
Plastic Mold Components
Plastic Mold Components
Show all categories of Plastic Mold Components-
Ejector Pins
-
Sleeves, Center Pins
-
Core Pins
-
Sprue bushings, Gates, and other components
-
Date Mark Inserts, Recycle Mark Inserts, Pins with Gas Vent
-
Undercut, Plates
-
Leader Components, Components for Ejector Space
-
Mold Opening Controllers
-
Cooling or Heating Components
-
Accessories, Others
-
Components of Large Mold, Die Casting
-
-
Injection Molding Components
Injection Molding Components
Show all categories of Injection Molding Components-
Purging Agent
-
Injection Molding Machine Products
-
Accessories of Equipment
-
Auxiliary Equipment
-
Air Nippers
-
Air Cylinders
-
Air Chuck for Runner
-
Chuck Board Components
-
Frames
-
Suction Components
-
Parallel Air Chuck
-
Special Air Chuck
-
Mold Maintenance
-
Heating Items
-
Heat Insulation Sheets
-
Couplers, Plugs, One-touch Joints
-
Tubes, Hoses, Peripheral Components
-
- Webcode Seach | Series
-
#CODE
- Discontinued Products
Loading...
- inCAD Library Home
- > No.000129 Compact Workpiece Transfer
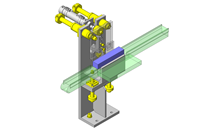
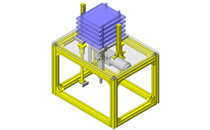
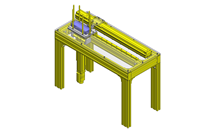
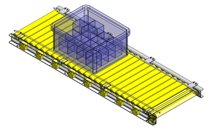
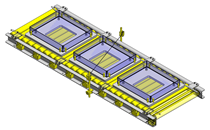
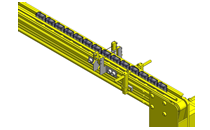
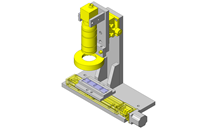
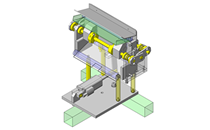
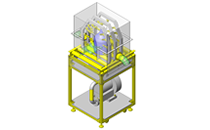
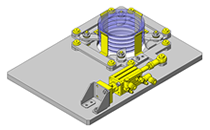
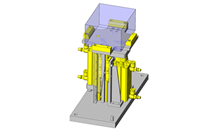
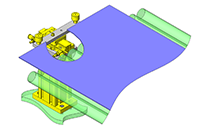
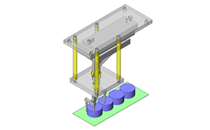
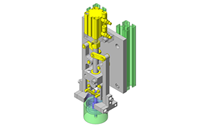
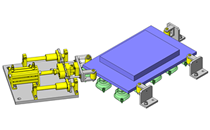
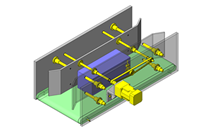
No.000129 Compact Workpiece Transfer
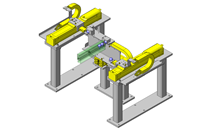
Extrusion Mechanism utilizing a linear guide
Relevant category
- * Unit assembly Data consists of some sub-assemblies.
It is configured so that each sub-assembly unit can be used as it is or edited.
Application Overview
Purpose
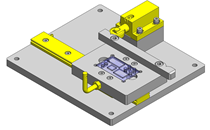
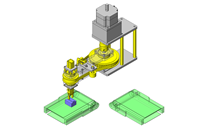
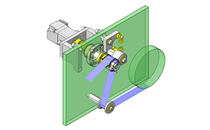
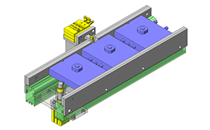
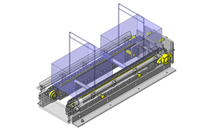
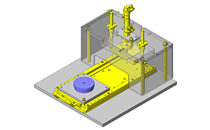
- A design where the linear guide is fixed and the rail moves to help avoid interference. A pusher attached to the end of the rail pushes the workpiece into the transfer box.
Points for use
- Useful in designs where air cannot be used to power the transfer mechanism.
Target workpiece
- Resin magazine (resin pallet)
- Outer dimensions: W67 x H70 x D80 mm
- Workpiece weight: 170 g x 3 pieces = 510 g
Design Specifications
Operating Conditions or Design Requirements
- Outer dimensions: W663 x H373 x D164 mm
- Single axis robot stroke: 300 mm [movable stroke: 229 mm]
Required Performance
- Workpiece transfer positioning accuracy: ±0.1 mm
- Required workpiece transfer load capacity: 2.4 kg
- Workpiece transfer speed: 350 mm/s
Selection Criteria for Main Components
- Single axis robot
- A single axis robot that satisfies "maximum load capacity ≥ movable part mass + workpiece weight".
- A robot that satisfies the transfer speed specification and is reasonably priced.
- A robot that satisfies the transfer stroke.
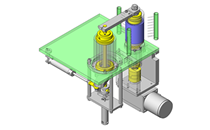
- Linear Guides
- Linear guides that satisfy the allowable moment.
Design Evaluation
Verification of main components
- Whether the linear guides withstand the loading moment and whether the robot is suitable for the transfer specifications (load capacity, speed, stroke) are verified.
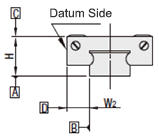
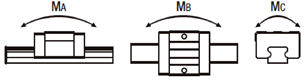
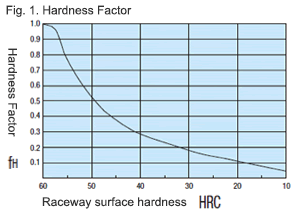
- Linear guide allowable moment
- Linear guide allowable moment: MB = 104 N·m (yawing)
- Single axis robot maximum push force: f = 150 N
Distance from rotation center to acting point: I = 0.136 m
Safety factor: e = 5 times
Loading moment: M = 150 N x 0.136 = 20.4
Required allowable moment: MB > M x e = 20.4 x 5 = 102 N·m
Therefore, linear guides with allowable moment of 104 N·m are selected.
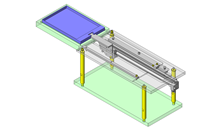
- Transfer mass: 2.25 kg
- Linear guide rail: 0.92 kg, slide plate: 0.58 kg, pan: 0.32 kg, claw holder: 0.37 kg, claw: 0.06 kg
- Workpiece mass: 0.17 kg x 3 pieces = 0.51 kg
- Friction coefficient: 0.3 (tentative value)
- Required operation power: workpiece mass x friction coefficient = 0.51 kg x 0.3 = 0.153 kg
- Required transferable mass
- 2.25 kg + 0.153 kg = 2.403 kg < 25 kg (single axis robot maximum load capacity)
- Required speed
- 1 cycle: 3 s
Required speed = (transfer distance x 2) ÷ 3 = 458 mm ÷ 3 s = 153 mm/s
As acceleration/deceleration time is not considered in this equation,
Acceleration: 0.1 G = 980 mm/s² (tentative value)
Setting speed: 350 mm/s < 500 mm/s (single axis robot maximum speed)
Acceleration time = speed ÷ acceleration = 350 mm/s ÷ 980 mm/s² = 0.33 s
Moving distance during acceleration/deceleration = acceleration x acceleration time ÷ 2 = 980 mm/s² x 0.33 s ÷ 2 = 53.4 mm
Moving distance at setting speed = distance per cycle - moving distance per cycle during acceleration/deceleration = 229 mm x 2 - 53.4 mm x 4 = 244.4 mm
Moving time at setting speed = moving distance at setting speed ÷ setting speed = 244.4 mm ÷ 350 mm/s = 0.77 s - 1 cycle = 0.77 s + 0.33 s x 4 = 2.09 s
- Marginal time: 3 s - 2.09 s = 0.91 s
- 1 cycle: 3 s
Other Design Consideration
- Since linear guide is mounted directly above the workpiece transfer table, a drip pan is installed to catch excess grease.
Explore Similar Application Examples
-
Relevant category
-
Relevant category